Maize varieties and their root trait variation mediate the development of rhizosphere arthropod diversity.
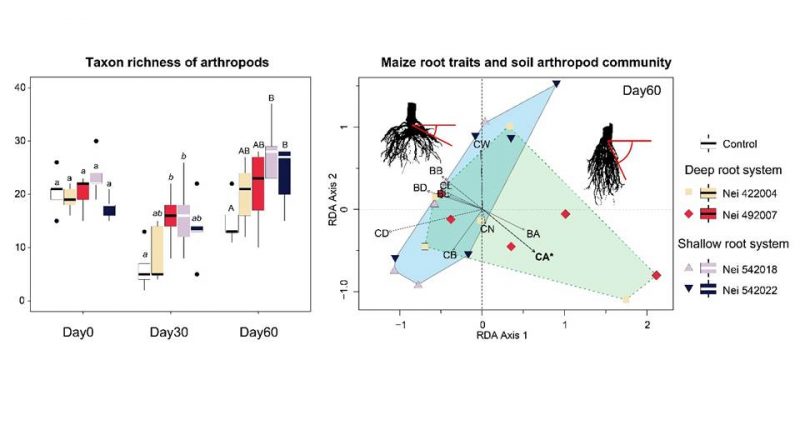
While ecological roles of rhizosphere arthropods are well documented, little is known about the relationship between the development of plant roots and soil arthropod communities in agroecosystems. In this study, we investigated the effects of maize varieties and their root traits on the diversity and community composition of soil arthropods over time. Soil arthropods and root traits were evaluated before planting and at 30 and 60 days after planting in four maize varieties with different root growth angles and lateral root branching. Arthropod diversity declined from day 0 to 30 but recovered by day 60 with the development of maize roots. Two maize varieties (Nei 542018 and Nei 542022) exhibited lower brace and crown root angles, and arthropod taxon richness was greater in these two varieties than in others. The highest abundance of detritivores and predators was found in one of the maize varieties (Nei 542018) which, in addition to lower root angle, attained greater root diameter and lateral root branching and length. Redundancy analysis indicated that soil arthropod composition was correlated with crown root angle. Our findings highlight the importance of root traits, especially the angle of the roots, to enhance arthropod biodiversity in the rhizosphere ecosystem.
แม้จะเป็นที่ทราบกันดีว่าสัตว์ขาปล้องในดินขนาดเล็กที่อาศัยอยู่บริเวณรากของพืชมีความสำคัญและมีบทบาททางนิเวศวิทยาต่อต้นพืช แต่ความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างการพัฒนาของรากพืชและชุมชนสัตว์ขาปล้องในดินในระบบเกษตรยังไม่ได้รับการศึกษามากนัก ในการศึกษานี้ผู้วิจัยศึกษาความแปรผันของรากข้าวโพด การเจริญและลักษณะของรากที่มีต่อความหลากหลายและองค์ประกอบของชุมชนของสัตว์ขาปล้องในดินเมื่อเวลาผ่านไป ทำการเก็บตัวอย่างสัตว์ขาปล้องในดินและลักษณะของราก 3 ช่วงเวลา คือ ก่อนปลูก หลังปลูกที่ 30 และ 60 วัน ในข้าวโพด 4 สายพันธุ์ที่มีมุมการเจริญของรากและการแตกแขนงด้านข้างที่ต่างกัน ผลการศึกษาพบว่า ความหลากหลายของสัตว์ขาปล้องลดลงจากช่วงก่อนปลูก ถึง หลังปลูกที่ 30 วัน แต่มีความหลากหลายมากขึ้นในวันที่ 60 พร้อมกับการเจริญของรากข้าวโพดที่มากขึ้น ข้าวโพดพันธุ์ Nei 542018 และ Nei 542022 มีการเจริญของรากที่แผ่ไปด้านข้าง ซึ่งสอดคล้องกับความหลากชนิดของสัตว์ขาปล้องที่พบในสองพันธุ์นี้มากกว่าพันธุ์อื่นๆ นอกจากนี้ยังพบความหลากหลายของสัตว์ผู้ล่าและสัตว์กินซากในข้าวโพดพันธุ์ Nei 542018 มากกว่าพันธุ์อื่น ซึ่งข้าวโพดสายพันธุ์นี้นอกจากจะมีมุมของรากที่ต่ำกว่าแล้ว ยังมีเส้นผ่านศูนย์กลางรากที่มากขึ้น การแตกแขนงและความยาวของรากด้านข้างที่มากขึ้น เมื่อเทียบกับพันธุ์อื่น นอกจากนี้การวิเคราะห์ Redundancy analysis บ่งชี้ว่าองค์ประกอบของสัตว์ขาปล้องในดินมีความสัมพันธ์กับมุมของรากฟัน ผลการศึกษาในครั้งนี้ เน้นให้เห็นความความสำคัญของลักษณะของราก โดยเฉพาะมุมของราก ที่มีผลเพิ่มความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์ขาปล้องในระบบนิเวศรอบรากของต้นพืช
Saowong, K., Saengwilai, P. J., Fuangarworn, M., Nakamura, A., Jeratthitikul, E. 2022. Maize varieties and their root trait variation mediate the development of rhizosphere arthropod diversity. Applied Soil Ecology. 180: 104615. Doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2022.104615.