Highlight Activities 2022: Foraging microhabitat selection of Spoon-billed Sandpiper in the Upper Gulf of Mottama, Myanmar.
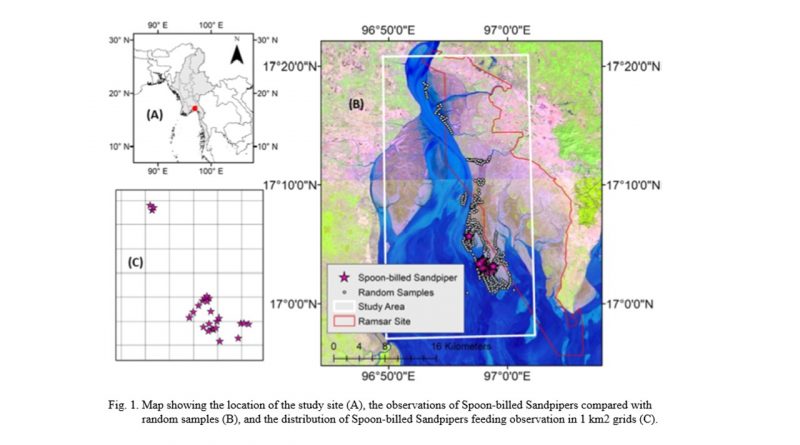
Abstract: The Gulf of Mottama, Myanmar, supports perhaps 60% of the global population of the Critically Endangered Spoon-billed Sandpiper (Calidris pygmaea).We identified macrohabitat and microhabitat characteristics of Spoon-billed Sandpiper foraging locations. We considered 1) location (relative to distance to the main river channel), 2) temporal use patterns (relative to the tide cycle), 3) physical substrate characteristics and 4) possible food sources. Spoon-billed Sandpipers were observed at 26 foraging locations during the study (November 2019-March 2020) and were found more frequently on mixed sand-mud substrate. Logistic regression models indicated that foraging locations were associated with shallow surface puddles, compared to random locations. The mixed sand-mud substrate supported more polychaetes relative to crabs or insect larvae, the three most common prey types in our 442 benthos samples used to assess prey availabilityThe Gulf of Mottama needs to be protected as an intact functioning estuary as it is a key site for Spoon-billed Sandpiper and other threatened shorebirds. We still lack understanding as to how potential prey availability is driving site selection and how these characteristics vary among wintering sites.
Pyae Phyo Aung, Buchanan, G. M., Round, P. D., Zockler, C.., Kelly, C., Naruemon Tantipisanuh & Gale, G. A. 2022 Foraging microhabitat selection of Spoon-billed Sandpiper in the Upper Gulf of Mottama, Myanmar. Global Ecology and Conservation e02077