Highlight Activities 2022: Coxiella-like bacteria in Haemaphysalis wellingtoni ticks associated with Great Hornbill, Buceros bicornis
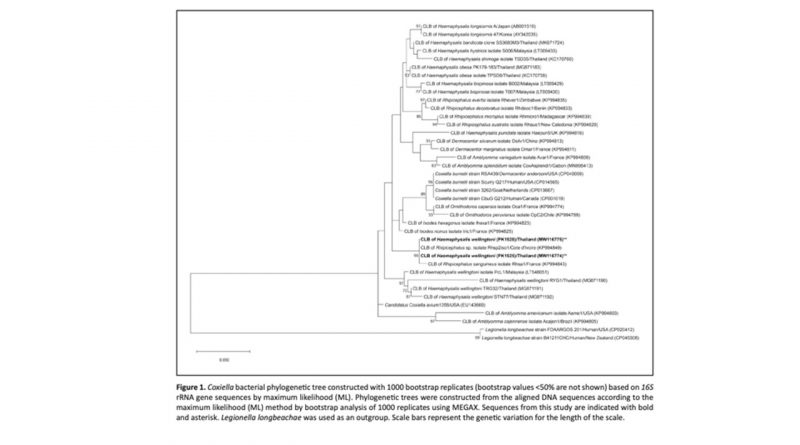
Summary: Birds are known to be the most mobile hosts and are therefore considered to be hosts with potential to contribute to the long-distance spread and transmission of tick-borne pathogens. In the present study, ticks were collected from a hornbill nest at Chaiyaphum Province, Thailand. They were screened for the presence of Coxiella bacteria using conventional PCR. The evolutionary relationships of positive Coxiella-like bacteria (CLB) were analysed based on the gene sequences of 16S rRNA, groEL and rpoB. Among all 22 tested ticks, CLB infections were found in 2 Haemaphysalis wellingtoni individuals. In a phylogenetic analysis, the Coxiella 16S rRNA gene detected in this study formed a separate clade from sequences found in ticks of the same genus. In contrast, the phylogenetic relationships based on groEL and rpoB revealed that these two genes from H. wellingtoni ticks grouped with CLB from the same tick genus (Haemaphysalis). This study is the first to report the presence of CLB in H. wellingtoni ticks associated with the Great Hornbill, Buceros bicornis in Thailand. Three genes of CLB studied herein were grouped separately with Coxiella burnetii (pathogenic strain). The effects of CLB in the ticks and Buceros bicornis require further investigation.
Reference
Usananan, P., Kaenkan, W., Trinachartvanit, W., Baimai, V., & Ahantarig, A. (2022). Coxiella-like bacteria in Haemaphysalis wellingtoni ticks associated with Great Hornbill, Buceros bicornis. Tropical biomedicine, 39(2), 191–196. https://doi.org/10.47665/tb.39.2.009