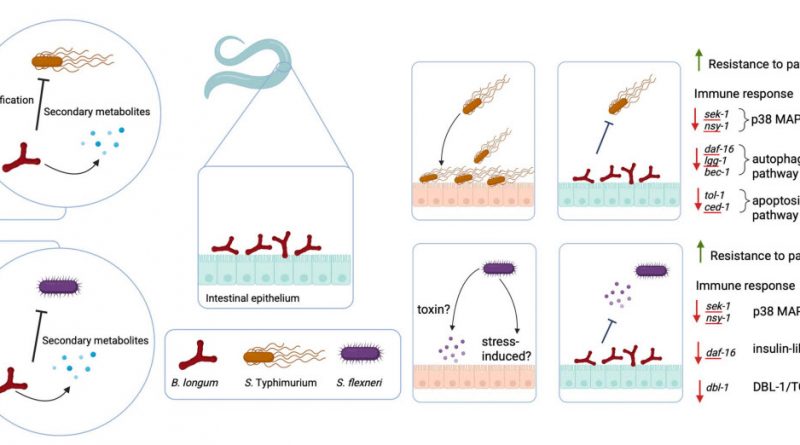
Highlight Activities 2025: Gut commensal Bifidobacterium longum confers resistance to Salmonella Typhimurium and Shigella flexneri in a Caenorhabditis elegans model
This study investigated alternative, non-antibiotic treatments for enteric infections caused by the two main pathogenic bacteria, which are classified as high-priority antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Our screening result shows the bacteria from a collection of human gut bacteria, Bifidobacterium longum, represents the most effective species for inhibiting both pathogens. Morever, the result on simple animal experiments also found that B. longum protects the host from bacteria infection. The protective effects is suggested to involve with host immune modulation. Overall, our findings suggest that the common gut microbe B. longum holds potential as a natural, non-antibiotic therapeutic for controlling bacteria infections.
งานวิจัยนี้มุ่งเน้นไปที่การใช้การรักษาทางเลือกที่ไม่ใช้ยาปฏิชีวนะสำหรับโรคติดเชื้อในลำไส้ที่เกิดจากแบคทีเรียก่อโรคหลักสองชนิดอยู่ในกลุ่มเชื้อก่อโรคดื้อยาปฏิชีวนะที่มีความสำคัญสูง ผลการทดลองพบว่าแบคทีเรียที่ได้จากการคัดกรองจากกลุ่มแบคทีเรียปกติที่พบได้ในลำไส้ของมนุษย์ที่มีชื่อว่า Bifidobacterium longum เป็นสายพันธุ์ที่มีประสิทธิภาพมากที่สุดในการยับยั้งเชื้อก่อโรค นอกจากนี้ ผลการทดลองในสัตว์เบื้องต้นยังพบว่า B. longum ช่วยปกป้องสัตว์ทดลองจากการติดเชื้อแบคทีเรียได้ โดยสันนิษฐานว่าผลการป้องกันนี้เกี่ยวข้องกับการปรับเปลี่ยนระบบภูมิคุ้มกันของสัตว์ทดลอง ผลการศึกษาของงานวิจัยนี้ชี้ให้เห็นว่าจุลินทรีย์ในลำไส้ทั่วไปอย่าง B. longum มีศักยภาพในการยับยั้งเชื้อก่อโรคที่สามารถนำไปพัฒนาต่อยอดเป็นวิธีการรักษาตามธรรมชาติที่ไม่ใช้ยาปฏิชีวนะสำหรับการควบคุมการติดเชื้อแบคทีเรียได้ในอนาคต