Highlight Activities 2022: A new record of Rickettsia japonica in ticks infesting a Burmese ferret-badger in Thailand
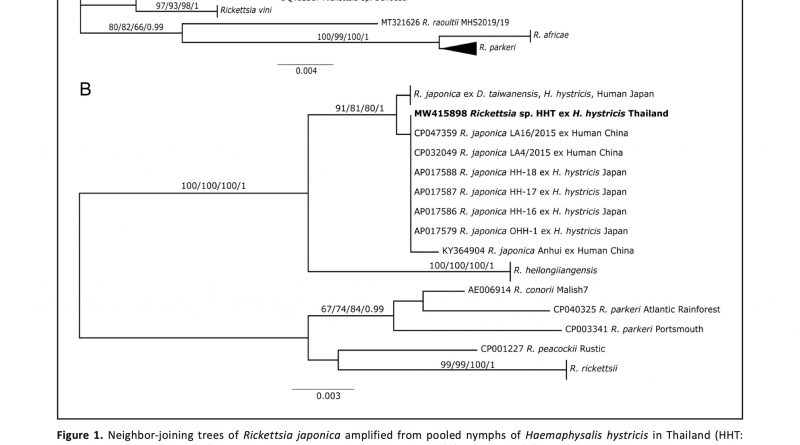
Summary: Ticks are important vectors of arthropod-borne diseases and they can transmit a wide variety of zoonotic pathogens to humans, domestic and wild animals. Rickettsia japonica is a member of SFG rickettsiae causing Japanese spotted fever (JSF) and can transmit to humans via infected ticks. In this study, we report the first case of Rickettsia japonica in Haemaphysalis hystricis tick collected from a roadkill Burmese ferret-badger (Melogale personata) in Loei province, northeastern Thailand. According to the DNA sequences and phylogenetic analyses of the outer membrane protein A and B genes (ompA and ompB), the detected R. japonica was identical to those found in JSF patients in Korea, Japan, and China, and closely related to Rickettsia detected by ompA in a tick from Thailand. Further study on the prevalence of R. japonica and diversity of mammalian reservoir hosts will be useful to gain a better understanding of JSF epidemiology.
Reference
Hirunkanokpun, S., Ahantarig, A., Baimai, B., Pramual, P., and Trinachartvanit, W. (2022). A new record of Rickettsia japonica in ticks infesting a Burmese ferret-badger in Thailand. Tropical biomedicine, 39(1), 55–59. https://doi.org/10.47665/tb.39.1.007